You can protect you skin to over exposure by wearing proper clothing and/or sunscreen. Sunscreen with a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of 30 blocks out most of the harmful UV radiation. A sunscreen with an SPF 30 means that you can stay out in the sun 30 times longer than you can with no protection before you skin begins to turn pink.
|
|
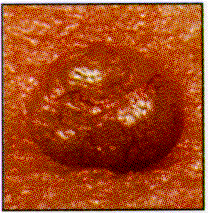
Basal Cell Carcinomas begins as small shiny bumps and grows slowly. It is the most common form of skin cancer. |
|
|
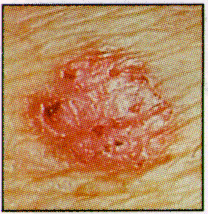
Squamous Cell Carcinoms is another common form of skin cancer. When these tumors first appear they are firm to the touch. They, like the basal cell carcinomas, appear most often on sun- exposed areas of your body. |
|
|
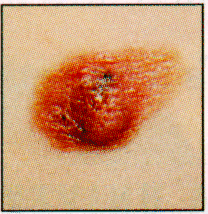
Malignant Melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer. Malignant melanoma, like basal and squamous carcinomas, is linked to overexposure to the sun; however, it can appear any place on your body. When detected early and with proper treatment, the recovery rate from this form of skin cancer can be very high. |
|
|
Advanced Stage
|
UV - its not all bad.
Fortunately, if detected early, the cancers
listed above can be treated. DO NOT PANIC. Sunshine is also good for us! It
makes us cheery. UV radiation plays a role in the our body's
production of vitamin K. A lack of Vitamin K can lead to liver damage and
jaundice. Green leafy vegetables are one common source of vitamin K. So your
parents were right -"Eat your vegetables." Speaking of plants, UV
radiation is important in pollination of certain plants. Some insects, such
as honeybees, find reflected UV light by some plants alluring. Some spiders
take advantage of the alluring nature of reflected UV radiation to some
insects by including strands in their web that are UV reflective, and thus
also alluring.
Your risk of skin cancer is related to the amount of time you spend in the sun and your skin type. The amount of UV radiation that you are exposed to depends on:
Your risk of skin cancer is related to the amount of time you spend in the sun and your skin type. The amount of UV radiation that you are exposed to depends on:
How high the sun is in the sky. This is a
function of
Season
- Greatest exposure of UV light in the summer.
Latitude
- Strongest UV concentration in tropical locations near the equator.
Time
of Day - Most intense UV radiation occurs between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m.
Altitude: UV concentrations increase the
higher the altitude.